Living Organisms Use Osmoregulation to Balance
Many marine organisms have internal solute concentrations that are similar to their environment. Water constantly leaves and goes into the cells.
Salt Regulation In Freshwater And Seawater Fishes Blogionik
Osmoregulation is the process of maintenance of salt and water balance osmotic balance across membranes within the bodys fluids which are composed of water plus electrolytes and non-electrolytes.
. Many marine organisms have internal solute concentrations that are similar to their environment. That is to compensate for water loss avoid excess water gain and maintain the proper osmotic concentration osmolarity of the body fluids. Living organisms use osmoregulation to balance solute and water concentrations in their cells tissues and organs.
Many marine organisms have internal solute concentrations that are similar to their environment. However this is not typically true of freshwater and terrestrial organisms. Plants growing in hydrated soils compensate water loss by.
Many marine organisms have internal solute concentrations that are similar to their environment. However this is not typically true of freshwater and terrestrial organisms. Living organisms use osmoregulation to balance solute and water concentrations in their cells tissues and organs.
Not all solutes can pass through a semi-permeable membrane. Osmoregulation in Animals. Animal cells require a more critical balance of water and solutes in the body as they cannot survive a net water gain or loss.
A non-electrolyte in contrast doesnt dissociate into ions. Osmoregulation and osmotic balance are important bodily functions resulting in water and salt balance. Organisms require osmoregulation to maintain a constant and proper osmotic pressure within the body or cell.
Many marine organisms have internal solute concentrations that are similar to their environment. Living organisms use osmoregulation to balance solute and water concentrations in their cells tissues and organs. An electrolyte is a solute that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
Osmoregulation maintains the proper balance of electrolytes in the human body despite external factors such as temperature diet and weather conditions. Osmosis is the movement of water across the membrane. Many structures and organs are involved in osmoregulation including the skin gills digestive tract cloaca kidneys and bladder.
Even terrestrial organisms consist of over. The physiological processes that an organism uses to maintain water balance. Osmoregulation is the process of maintenance of salt and water balance osmotic balance across membranes within the bodys fluids which are composed of water plus electrolytes and non-electrolytes.
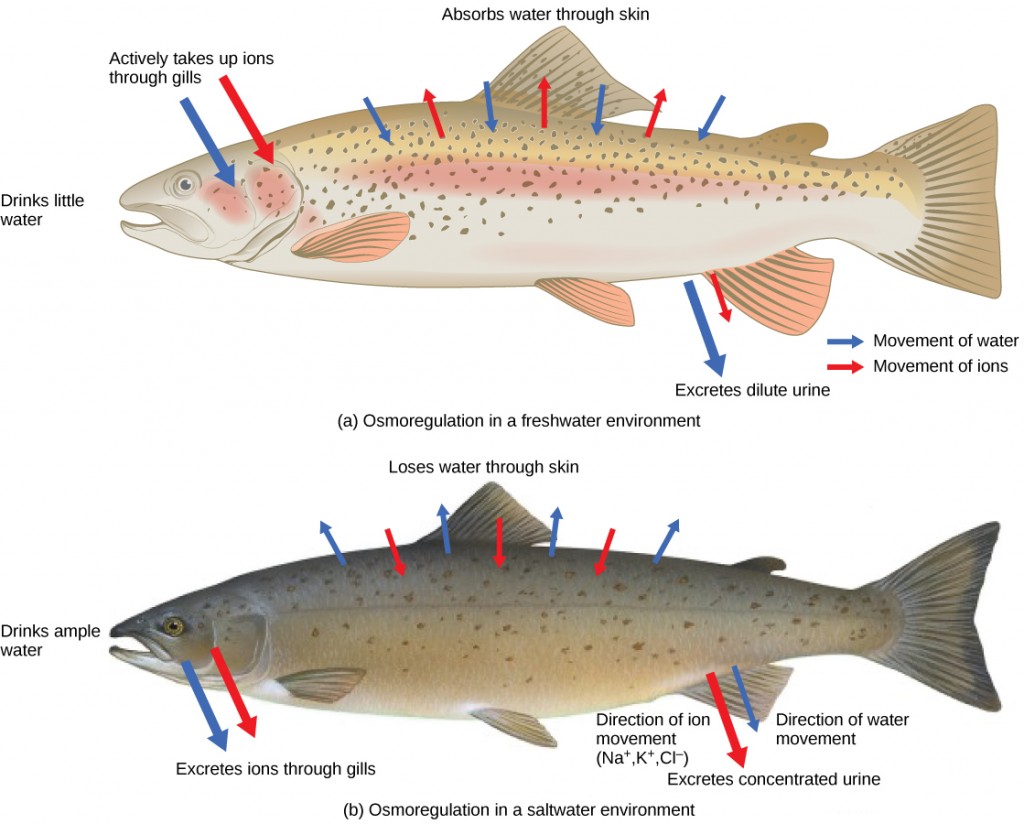
However the quantity of the water and the solutes is kept in balance. Living organisms use osmoregulation to balance solute and water concentrations in their cells tissues and organs. There is always a difference between the salinity of a fishs environment and the inside of its body.
Living organisms use osmoregulation to balance solute and water concentrations in their cells tissues and organs. However this is not typically true of freshwater and terrestrial organisms. Life began in water and water is vital to the chemistry of life.
The fluids inside and surrounding cells are composed of water electrolytes and nonelectrolytes. Osmosis occurs to equalize the number of solute molecules across a semi-permeable membrane by the movement of water to the side. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane in response to osmotic pressure caused by an imbalance of molecules on either side of the membrane.
By diffusion of water or solutes osmotic balance ensures that optimal concentrations of electrolytes and non-electrolytes are maintained in cells body tissues and in interstitial fluid. Bacteria use a transport mechanism to absorb electrolytes when osmolarity around it increases. A fish is after all a collection of fluids floating in a fluid environment with only a thin skin to separate the two.
An electrolyte is a compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water. How Fish Maintain an Internal Balance of Salt and Water. However this is not typically true of freshwater and terrestrial organisms.
However this is not typically true of freshwater and terrestrial organisms. There are two methods for keeping this balance. Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance osmotic balance across membranes within the body.
Plants use stomata on the lower side of their leaves to regulate water loss. Osmoregulation the control of water and salt balance presents different challenges to organisms living in fresh water salt water and aerial or terrestrial environments Fig. The osmotic stress activates certain genes in bacteria that synthesize osmoprotectants.
Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining an internal balance of salt and water in a fishs body. Water potential regulation within a cell or organism maintains fluid and electrolyte balance in proportion to the surrounding environment.

4 1 Osmoregulation In Animals Living In Aquatic Environment Introductory Animal Physiology
11 1 Homeostasis And Osmoregulation Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
4 1 Osmoregulation In Animals Living In Aquatic Environment Introductory Animal Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment